When inheriting, inheritance tax must be paid on the taxable portion of the estate. How much are they between spouses, Pacs partners? What exceptions and deductions are possible? How is this tax calculated?
Inheritance tax in France
In France, property transferred after death is subject to inheritance tax.
Each heir must pay tax calculated according to his share of the inheritance. Thus, the calculation of inheritance tax is carried out using scales characteristic of several categories of heirs. However, there are deductions and tax benefits provided by law for the deceased's spouses and family members.
When and where to pay inheritance tax?
Paying inheritance tax: who and to whom?
Payment of tax on inherited property must, in principle, be made immediately (in cash) in a lump sum, at the time of filing a declaration of the right to inheritance with the tax authorities at the place of residence of the deceased. It can be:
- or the public finance registration center SIE (Service des impôts des entreprises),
- or departmental registration service in large cities (Paris, Lyon, Bordeaux, Rennes, Grasse and Nice for the Alpes-Maritimes),
- or the land registry and registration service in certain departments (Dunkirque and Valenciennes for the Northern department, Montpellier and Béziers for Hérault, Draguignan and Toulon for the Var, Laon in Aisne, Digne-les-Bains for the Alpes-Haute-Provence, Gap for the Hautes-Alpes, Toulouse for Haute-Garonne, etc.),
- or Inland Revenue for Non-Resident Individuals (SIP NR) if the deceased lived abroad.
Any heir, as well as the donee, that is, the beneficiary of the gift or legatee (d'un legs), must fill out an application for inheritance after the death of the deceased. This is a duty, except in a few special cases. This is a document submitted to the tax authorities, which summarizes the composition of the estate (property, debts), as well as donations made before death.
The net assets (after deducting any debts) of the estate determine the rights that must be paid by each heir.
There are two cases of derogation from the obligation to fill out a declaration of succession:
- Lineal heirs (children), surviving spouse or PACS partner are exempt from the obligation to complete a declaration of inheritance when the total assets of the estate (assets without deduction of debts, liabilities) are less than €50,000, provided that they have not received a donation or gift (amount of money, jewelry, car), undeclared by the deceased.
- For any other beneficiary of the inheritance, if the gross assets of the immovable property are less than 3,000 euros, the inheritance declaration is not completed.
Form 2705 (Cerfa 11277*08), like Form 2705-C, 2705-A (for life insurance contracts) or 2709 (for real estate), can be completed and signed by one heir. He must submit it to the State Finance Center at the place of residence of the deceased or to the Tax Service of Non-Resident Individuals if the deceased lived abroad.
Deadline for payment and submission of declaration of succession
The heir has a period of 6 months to apply for succession after death if it occurred in metropolitan France, or one year otherwise. However, certain situations, such as the absence of an heir, the discovery of a will after death, a disputed inheritance, or not knowing the identity of one or more heirs on the date of death, can change this period.
Please note: any late application for inheritance is subject to a penalty. In case of delay, interest of 0.20% is applied every month from the end of the period, plus 10% if the deposit is determined more than 6 months late, or even 40% if the situation is not resolved after official notification from the tax authorities.
Inheritance tax amount
The calculation of inheritance tax is inevitable: any beneficiary of an inheritance is required to complete a declaration with payment of duties when submitting it to the tax office responsible for registration.
Inheritance tax: calculation in a few steps
- Determine net property assets
To be able to calculate inheritance tax, you must first determine the amount on which the tax should apply. This involves establishing the amount of the deceased's taxable net assets, which is then distributed to the heirs. It is on this net share that the tax authorities determine the amount of duties payable. Calculation of net taxable assets = assets – liabilities.
Asset composition: movable property (car, jewelry, furniture, cash, bars and coins in precious metals, bank accounts, passbooks, shares, etc.) and real estate (house, apartment, land, forests, etc. ). Some items are subject to partial or complete exemption.
Composition of obligations: Debts deducted from assets (unpaid medical expenses, funeral expenses, some taxes such as income tax or local taxes, etc.)
Attention! A pre-death gift made by the decedent to one or more heirs must be included in the estate for estate tax purposes if it was made less than 15 years ago. - Determine your taxable share according to your family relationship
In the absence of a will, the inheritance is distributed in accordance with the procedure established by law. Depending on your relationship to the deceased, you may be able to take advantage of a deduction that reduces your tax base for inheritance taxes. The principle is as follows: the closer the relationship, the larger the deduction. - Apply commission calculation scale
Once you know your taxable share, you must apply the inheritance tax schedule. This scale is progressive.
Inheritance tax calculator
To facilitate the calculation of inheritance rights, you can use a simulator.
 Since spring 2017 there is official simulator, which allows you to freely and anonymously calculate inheritance tax in the event of the death of a loved one. Using this calculator requires knowledge of several elements:
Since spring 2017 there is official simulator, which allows you to freely and anonymously calculate inheritance tax in the event of the death of a loved one. Using this calculator requires knowledge of several elements:
- tax residence of the deceased (in France or abroad),
- information about his situation (for example, if he was a victim of war or a terrorist attack),
- net value of assets, composition of inherited property (inherited property minus debts and the amount of the heir’s share in the inherited property.
You can also contact me for a consultation, at which I will make you a statement of the inheritance, calculate the share of each heir and the amount of tax.
Inheritance tax between spouses and partners PACS: exemption
Inheritance tax exemption for surviving spouse
For any inheritance opened on or after 22 August 2007, the surviving spouse of the deceased receives a full exemption from inheritance tax.
This applies to surviving spouses, as well as civil solidarity partners (Pacs), provided that the latter have made a will. If this is not the case, the Pacs partner will be considered a third party and will have to pay inheritance tax at rate 60% as if he were unrelated to the family of the deceased.
Conditions of release between siblings
Inheritance tax exemption is also available to brothers and sisters who meet the very following criteria:
- Be over 50 years of age at the time of inheritance or suffer from an illness that prevents him from working.
- Lived with the deceased for the last five years.
- Not married or legally separated at the time of opening of the inheritance.
Note. Beneficiaries of the exemption must provide all supporting documents and information necessary to substantiate their position.
In addition, the property of victims of terrorist attacks or war, soldiers, firefighters, police officers, gendarmes and customs officers is exempt from the tax.
Inheritance tax: direct heirs and other benefits
When inheriting, tax is calculated on the taxable share of each heir. As seen above, the tax benefit is full for spouses and PACS partners. However, partial tax exemption also exists in other cases:
- In a direct line, that is, between a parent and their child or, conversely, between a son/daughter and his father/mother, the tax-free amount is 100,000 euros.
- Between siblings, this tax deduction reaches €15,932.
- For a nephew or niece it drops to €7,967.
- Finally, for grandchildren, great-grandchildren or third parties such as a PACS partner, the benefit is limited to €1,594.
If the heir is disabled, an additional deduction amount of EUR 159,325 is added to the deductions granted due to his family relationship with the deceased.
If the deceased lived in France, all his assets are subject to inheritance tax. On the other hand, if the heir resides outside France, only the assets located in France are taxed.
In addition to the quality of the deceased and the beneficiary, the nature of the property being transferred is taken into account. In particular, the following are exempt from inheritance tax:
- transfer of life annuity (réversions de rentes viagères) between spouses or parents in a straight line,
- works of art, collectibles, etc., donated to the state with its approval,
- buildings included in the register of historical monuments.
Partial exemption is available for forestry or agricultural property (maximum 75%) or shares or interests in companies carrying out industrial, commercial, craft, agricultural or consulting services - up to 75%.
Life insurance (Assurance Vie) and inheritance rights
Assurance Vie is not included in the estate
The deceased's Assurance Vie payments do not form part of his estate upon his death. Thus, such contracts are not included in his estate for purposes of calculating the inheritance tax due to the heirs. Therefore, there is no need to include them in the declaration of inheritance submitted to the tax authorities.
The only exception to this principle is the absence of a beneficiary clause and therefore a designated beneficiary in the event of death, the life insurance is added to the estate and is subject to inheritance tax as such.
Taxation of Assurance Vie in case of death
Assurance Vie is in principle not subject to inheritance tax: it is subject to a different taxation in the event of the death of the insured, provided for in Article 990 I of the General Tax Code (CGI), for contributions made up to 70 years of age.
Pursuant to Article 757 B CGI, only amounts paid by the subscriber after his 70th birthday under an Assurance Vie contract entered into after 20 November 1991 are subject to inheritance tax, less €30,500 for all beneficiaries under the contract (common deduction for all beneficiaries). Therefore, only part of the payments above this allowance are subject to inheritance tax (premiums paid excluding capital gains and interest).
Inheritance tax scale in 2022
A progressive scale is applied to the taxable amount after deductions depending on the relationship with the deceased; the scales remained unchanged as of January 1, 2022.
Scale for heirs in a straight line.
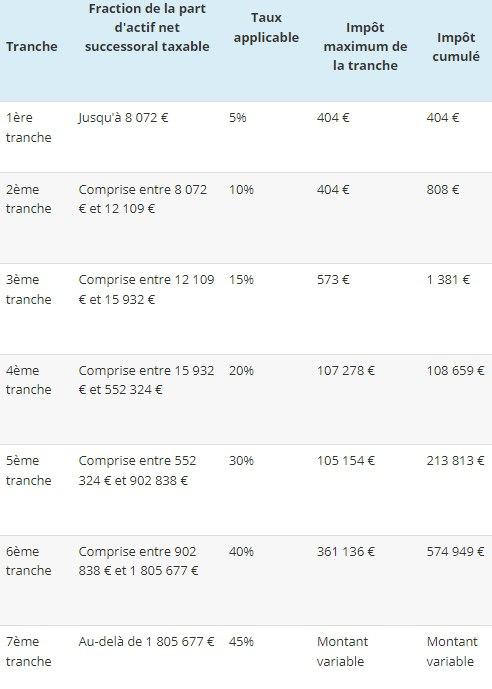
Between siblings the scale is as follows:
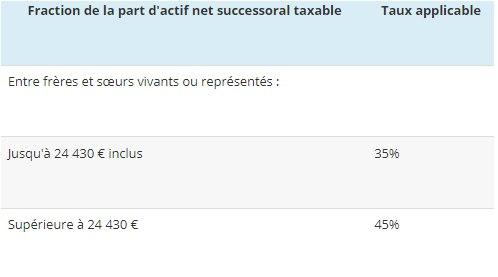
Between third parties or distant relatives, inheritance rights are established as follows:
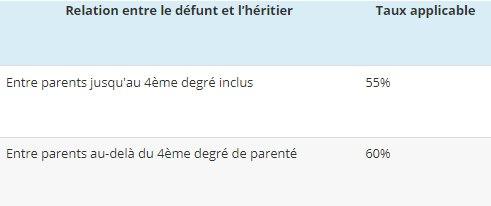
Source article 777 du CGI.
How to avoid or reduce inheritance tax?
If you have a taxable estate, it is impossible to avoid paying inheritance tax. However, there are many legal ways to reduce the amount in preparation for the transfer of assets. This means that the family must calculate future inheritance rights so that they know what to expect and can anticipate when making appropriate arrangements. Taxation is better controlled when you prepare to pass on an inheritance than when you endure it.
Examples of measures that need to be taken to reduce inheritance tax include the following (not an exhaustive list):
- Get married, when you live together: marriage allows the surviving spouse to be exempt from inheritance tax, while the cohabitant is not considered part of the family, even if the couple has children! Consequence: his share of the inheritance is taxed at the rate of 60% in excess of €1,594 of assets received (tax deduction amount).
- Give a gift to your children: A gift made more than 15 years ago is not taken into account when calculating inheritance tax. The tax efficiency of a donation can be optimized by donating only the title to the property.
- Signing an Assurance Vie agreement before the age of 70: An Assurance Vie opened before the age of 70 is exempt from inheritance tax, the amounts transferred are subject to favorable tax treatment (deduction of EUR 152,500 per beneficiary).
- Give traditional gifts: for a special occasion such as a birth, birthday, baptism, wedding or graduation - a gift for a child or grandchild. Attention, the value of the gift or the amount of money must be proportionate for each of the heirs.
- Investments in forest: Under certain conditions, forests are exempt from inheritance tax up to 75% of their value.
- Conclude pacte Dutreil : Under certain conditions, the value of the company transferred to its children can be reduced by three quarters by entering into an obligation to preserve the securities.
- Make a donation for your inheritance If you are an heir: Within 6 months of death, the heir can donate a sum of money to a general interest organization (association or foundation) to receive a tax deduction equal to the amount given. This technique, called gifting by inheritance (provided by section 788 CGI), allows you to reduce your taxable share while promoting a good cause.

However, be careful: taxation should not be the sole driver of the decision to transfer assets, you must consider your own objectives, the likely needs of the people you are transferring to, and comply with a specific set of civil and tax rules.
Source https://www.toutsurmesfinances.com/patrimoine/a/droits-de-succession-calcul-exoneration-bareme
